Role of Super-disintegrants in Tablets & Capsules: Does One Size Fit All?

Disintegration is the very first step in making the formulated active ingredient available for dissolution and absorption especially in case of solid oral dosage forms such as tablets and capsules. It is a crucial step that determines the rate at which the active becomes bioavailable to provide its therapeutic effect.
There are three primary mechanisms of disintegration: swelling, wicking, and shape recovery. In case of swelling, when tablet or capsule matrix comes in contact with the water, a fairly well distributed disintegrant particles swells multiple folds to its original volume, creating a strain and therefore a breaking force within the matrix that results in disintegration. These types are most effective with insoluble tablet matrices that allow resistance within the matrix responsible for the full disintegration. Examples of swelling disintegrants include alginic acid, sodium alginate, and sodium starch glycolate.
Wicking-type disintegrants work by drawing water into the matrix, creating channels that result in particle separation and ultimately matrix disruption and disintegration thus dissolving the matrix from within. These materials are usually fibrous in nature and typically used for soluble matrices. Examples include starch, croscarmellose, MCC, carboxymethyl cellulose, low-substituted HPC.
Shape-recovery disintegrants like crospovidone have excellent compressibility and they undergo plastic deformation during tablet compression. When in contact with the moisture, they bounce back to their original shape releasing the stored potential energy with expansion that ultimately creates a breaking force within the matrix and therefore disintegration. Crospovidone being non-ionic in nature, is useful as a pH-independent disintegrant.
Wicking or drawing of water or liquid into the powder compact is typically the first step when a dosage form comes in contact with the liquid medium following which depending on the nature of the disintegrant the subsequent process is governed.
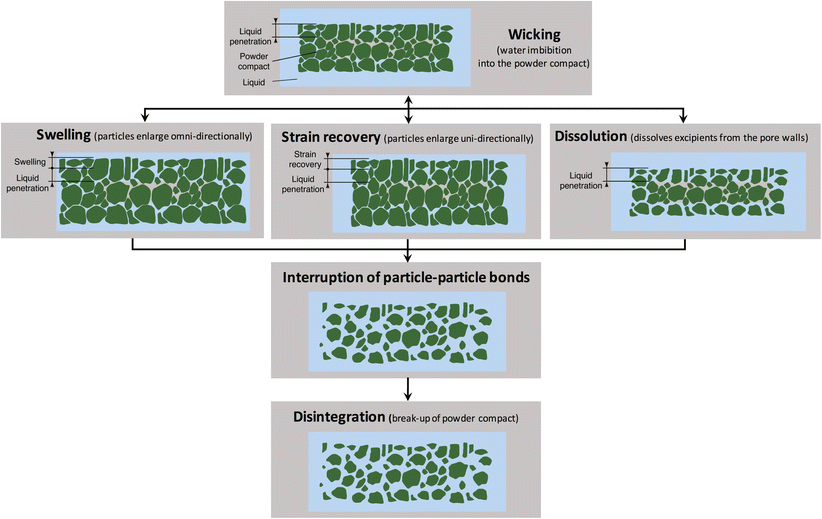
Figure: Disintegration mechanisms (Source: Pharm Res (2017) 34:890–917)
Finding the Right Super-disintegrant
Super-disintegrants: Conventional disintegrants like starch, and cellulose derivatives have been used traditionally with varying degrees of success. Depending on the mechanism of action, grade, and origin, the desired disintegration rate is achieved when these are used at higher concentrations (5 to >10%). This may cause additional tablet processing challenges, achieving the desired powder flow, compressibility, tablet weight, etc. Additionally, modern dosage forms such as orally disintegrating tablets or fast dissolve tablets require disintegrants that work rapidly, typically, in seconds. Super-disintegrants terminology has been assigned to the next generation of disintegrants based on their superior efficiency, flexibility in terms of applications, and low usage levels.
Sodium starch glycolate (SSG) and croscarmellose sodium (CCS) are the two most commonly used super-disintegrants. They are both synthesized from polymers of glucose. Starch is the backbone of SSG and cellulose in the case of CCS. Two primary chemical modifications are performed on starch and cellulose to enhance the disintegration efficiency. The introduction of carboxymethyl sodium groups allows water penetration and imparts cold water solubility, whereas, cross-linking of polymer backbone reduces both the water-soluble fraction and viscosity of the dispersion in water. The optimum balance between the degree of substitution and the extent of cross-linking allows for rapid water uptake without the formation of a viscous gel that might impede dissolution.
The choice of starch matters for SSG, with potato starch being the preferred option, while for CCS, particle size is crucial; coarser grades have been demonstrated to enhance efficiency. Both SSG and CCS can be used intra and extra-granularly and are effective as super-disintegrants in concentration between 1-5% for tablets.
Thus, the selection of the right disintegrant and concentration depends on several formulation and processing parameters and the desired finished product characteristics.
Quadra currently offers from Sigachi both Stargel® (SSG) synthesized from potato starch and HiLoseTM (CCS) that are of superior quality, GMP grade, and multi-compendial super-disintegrants for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical products.




